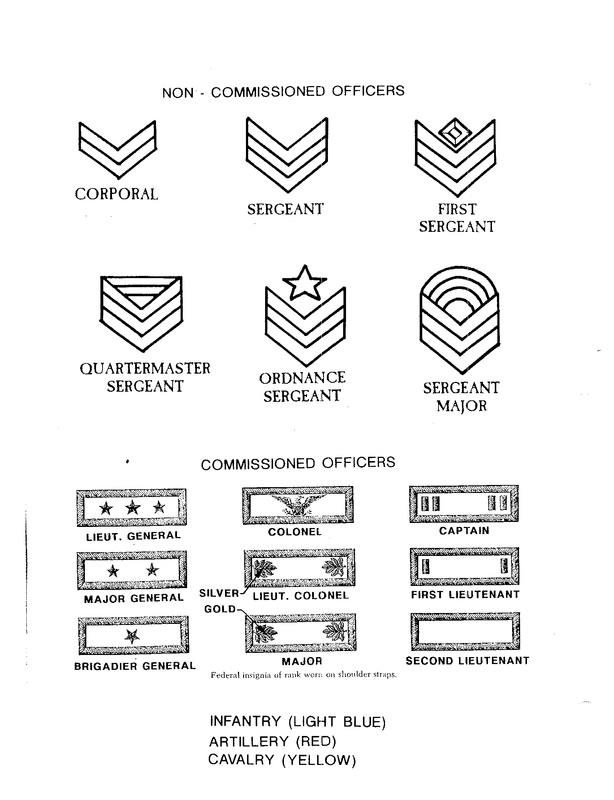
Rank Structure and Insignia
Composition of a Regiment
Ten companies, designated A-K. (J was skipped because the letters I and J look too similar and could be mistaken in handwriting of the day.)
Each company is commanded by a Captain, who is assisted by a First Lieutenant and a Second Lieutenant. These three are called "Line Officers" or "Company Officers".
Companies also have non-commissioned officers, or NCOs. Every Company has five Sergeants and eight Corporals. The "First Sergeant" is also called the "orderly Sergeant". The eight corporals serve in the ranks, while the sergeants (other than the First) and the two Lieutenants serve as "File Closers" behind the line of battle. A company might also have up to two Musicians, as well as a Wagoner (aka Teamster) to attend to the company wagon. The remainder of the company are Privates.
A company was split into two platoons, each supervised by one of the two Lieutenants.
Overall command of the regiment rested in the hands of the Colonel. He is assisted by the Lieutenant Colonel and Major. These three officers are known as "Field Grade" officers.
The regiment also had a number of staff positions. These included the Adjutant (rank of 2nd Lt.), the Quartermaster (2nd lt.), a Surgeon and two Assistant Surgeons. Regiments were also allowed to have a Chaplain who carried the acting rank of major.
Non-commission officers also served in staff positions. The Sergeant Major assisted the Adjutant in overseeing the company records and paper work; the Quartermaster Sergeant and Commissary Sergeant assisted the Quartermaster in handling the regiment's equipment and rations. The Hospital Steward assisted the surgeons.
The total paper strength of a regiment was approximately 1,000 men. There were very few times that regiment went into battle anywhere near that strength. After a couple of months in the field, even without seeing any combat, a regiment would be down to 600-700 men due to sickness. By mid-war, most regiments operated with an effective strength of between 250 and 500 men.
Army Organization
A regiment would be known by its number and state, as well as its brigade, division, corps and army placement. For example, at Gettysburg, the 140th NY was part of the Third Brigade, Second Division, Fifth Corps of the Army of the Potomac.
Ten companies, designated A-K. (J was skipped because the letters I and J look too similar and could be mistaken in handwriting of the day.)
Each company is commanded by a Captain, who is assisted by a First Lieutenant and a Second Lieutenant. These three are called "Line Officers" or "Company Officers".
Companies also have non-commissioned officers, or NCOs. Every Company has five Sergeants and eight Corporals. The "First Sergeant" is also called the "orderly Sergeant". The eight corporals serve in the ranks, while the sergeants (other than the First) and the two Lieutenants serve as "File Closers" behind the line of battle. A company might also have up to two Musicians, as well as a Wagoner (aka Teamster) to attend to the company wagon. The remainder of the company are Privates.
A company was split into two platoons, each supervised by one of the two Lieutenants.
Overall command of the regiment rested in the hands of the Colonel. He is assisted by the Lieutenant Colonel and Major. These three officers are known as "Field Grade" officers.
The regiment also had a number of staff positions. These included the Adjutant (rank of 2nd Lt.), the Quartermaster (2nd lt.), a Surgeon and two Assistant Surgeons. Regiments were also allowed to have a Chaplain who carried the acting rank of major.
Non-commission officers also served in staff positions. The Sergeant Major assisted the Adjutant in overseeing the company records and paper work; the Quartermaster Sergeant and Commissary Sergeant assisted the Quartermaster in handling the regiment's equipment and rations. The Hospital Steward assisted the surgeons.
The total paper strength of a regiment was approximately 1,000 men. There were very few times that regiment went into battle anywhere near that strength. After a couple of months in the field, even without seeing any combat, a regiment would be down to 600-700 men due to sickness. By mid-war, most regiments operated with an effective strength of between 250 and 500 men.
Army Organization
- 4 regiments constituted a Brigade (per regulations, commanded by a Brigadier General)
- 3-4 brigades constituted a Division (commanded by a Major General)
- 3 divisions constituted an Army Corp (commanded by a Major General)
- 3-7 corps constituted an Army (also commanded by a Major General)
A regiment would be known by its number and state, as well as its brigade, division, corps and army placement. For example, at Gettysburg, the 140th NY was part of the Third Brigade, Second Division, Fifth Corps of the Army of the Potomac.
Company Roster |
Regimental Roster |
|
1 Captian
1 First Lieutenant 1 Second Lieutenant 1 First (Orderly) Sergeant 4 Sergeants 8 Corporals 2 Musicians 1 Wagoner 82 Privates TOTAL: 101 |
1 Colonel
1 Lieutenant Colonel 1 Major 1 Adjutant (2nd Lt.) 1 Surgeon 2 Assistant Surgeons 1 Chaplain 1 Sergeant Major 1 Quartermaster Sergeant 1 Commissary Sergeant Plus Company Staffing |
1 Hospital Steward
2 Principal Musicians 10 Captains 10 First Lieutenants 10 First Sergeants 40 Sergeants 80 Corporals 20 Musicians 10 Wagoners 820 Privates TOTAL: 1,025 |